P-S Tapes | A Converter’s Guide
- Published: January 08, 2013, By Ann Hirst-Smith
Pressure-sensitive specialty tapes have, since their relatively recent arrival, contributed significantly in the holding, fastening, and joining sectors. Their achievements represent a combination of the benefits of high-technology pressure-sensitive adhesives and the ease and accuracy of handling and conversion of the pressure-sensitive laminate. By replacing mechanical fasteners in electrical and electronic goods and various automotive components, they have enabled considerable “downsizing” and streamlining, and in the medical and hygiene markets, have delivered innovation in the structure of hypoallergenic and non-toxic medical disposables, as well as enhanced levels of personal/patient comfort with the applied product.
The pressure-sensitive specialty tape industry has evolved over the years to become highly developed, diversified, and competitive, and the new AWA Alexander Watson Assoc. global study analyzes its strengths, weaknesses, and other characteristics across the value chain, setting it in the context of the overall pressure-sensitive tape market, which also encompasses packaging, masking, and consumer tapes.
Specialty tapes represent only 14% of total tape demand. They are, however, at the heart of a growing and profitable converting industry with a unique value chain that takes in every type of company from international pressure-sensitive laminators through commercial adhesive coaters, regional and local distributors, who may also be converters/die-cutters, and traditional converting companies.
Materials, technologies, markets
The AWA study tracks trends in the market by tape format, materials, technologies, and end uses, as well as by the world’s geographical regions. Market demand and production spans high-volume roll products and low-volume specialist die-cuts—such as gaskets—which may incorporate differential adhesives on two sides of a carrier tape as well as a release liner. There is, therefore, plenty of scope for converters to develop their own particular market niches.
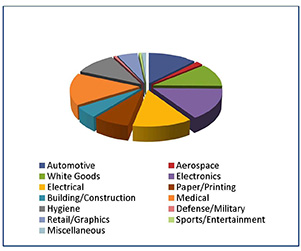
It is worth noting that there are opportunities for pressure-sensitive specialty tapes in all the world’s major manufacturing industries. AWA identifies as key sectors such markets as automotive, aerospace, white goods and other electrical products, electronics, paper and printing, building and construction, defense and military applications, retail, sports and entertainment, and medical and hygiene. Figure 1 shows the relative share of these end-use markets around the globe.
Regional differences
Different geographies, however, have different market profiles, and this is particularly evident with specialty tapes. Asia is a prime example. With its world-leading manufacturing base in automotive, technical electronic components, electrical products, and white goods, it is hardly surprising that it represents 39% of global demand for specialty tapes and grew more than 4% in 2011 (see Figure 2). Growth is driven not only by the lively demand from Asia’s domestic and regional markets, but by an increasing participation in export markets serving North American and European consumers.
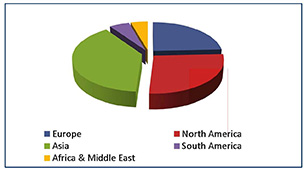
After Asia, North America is the largest user of pressure-sensitive specialty tapes. Alongside Europe, it is among the most mature markets, and in both regions, the prevailing economic climate has meant slowing growth—about 1.5% in the medium term for North America and about 2.5% for Europe—in many end-user sectors. Drivers of growth in both these regions will be a resurgence of volumes in automotive manufacturing forecast from 2013; sustained growth in the medical and hygiene markets; and consolidation of the use of these tapes to replace traditional mechanical fastening devices.
In South America, representing just 5% of global tape consumption, but exhibiting more than 5% growth in 2011, the developing consumer market (particularly in Brazil) has meant that end uses for specialty tapes in the region are focused on the hygiene, medical, and paper/printing sectors. These are the market segments that characterize emerging economies and will unquestionably influence opportunities for specialty tapes in the world’s remaining developing economies, such as Africa and the Middle East.
Structure of a specialty tape
Specialty tapes use a variety of materials to deliver their various functionalities—adhesive, carrier, and siliconized release liner in most configurations. Choice of all tape components is predicated on the end use, combined with cost considerations. The majority of tasks around the globe employ paper carriers and release liners, but films are growing (especially in the developed markets for advanced technical tasks), from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) (a leading choice in the hygiene market) to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyamide (PA). Nonwovens are widely used in medical applications, and foams perform additional functions in sound and vibration insulation in, for example, building and construction, automotive, and electronics.
Adhesive technologies differ by user requirements. The highest performance in terms of durability and resistance to environmental influences is delivered by solvent acrylic adhesives, and widely used on the medium- and low-surface energy plastics [such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polycarbonates] used in the electronics and electrical goods industries. In North America, such applications amount to nearly one-third of specialty tape usage, reflecting the market’s high manufacturing volumes of consumer electronics goods. Water-based adhesives are the choice for most everyday applications, with the high-temperature resistance and good environmental characteristics [no volatile organic compounds (VOCs)] of hot melt adhesives the third choice in adhesive technologies.
Release liners vary by the requirements of the application in terms of conversion—especially die-cutting—and end use, and they may be calendered kraft paper (glassine), clay coated paper, poly-coated paper, or film.
The value chain for specialty tapes is very flexible, so converters with a specialism in particular end-use markets as well as distributors can source tape products from today’s international tape laminators to meet product manufacturers’ needs across a wide spectrum of markets. Concluding with a supplier directory, Global Specialty Pressure-sensitive Tapes Market Study & Sourcebook 2012 provides a worldwide insight into the structure and nature of the market for pressure-sensitive specialty tapes that will benefit all levels of the value chain.